Neuralink reports an issue with its first human brain implant.
Last month, Neuralink broadcasted a nine-minute video featuring Arbaugh demonstrating the functionality of their Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) technology. During the video, Arbaugh was seen playing video games by simply imagining the cursor’s movements, which were then executed by the device.
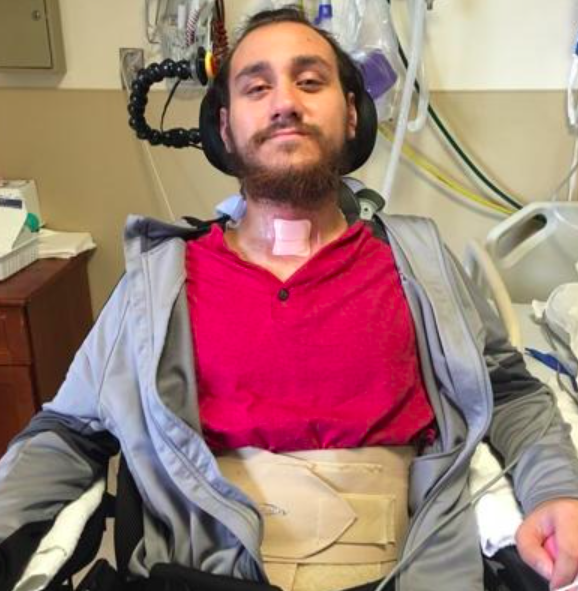
The Neuralink chip is equipped with 1,024 electrodes distributed across 64 threads, each thinner than a human hair, designed to collect brain activity data and send it to a computer for decoding, thus converting thoughts into actions. However, since the video’s release, some threads have retracted from Arbaugh’s brain, leading to fewer effective electrodes, Neuralink disclosed in a recent blog post, first reported by The Wall Street Journal. This retraction has hindered the company’s ability to gauge the system’s performance. In response, Neuralink has updated the recording algorithm to better detect neural signals and improved the user interface, aiming to increase the precision of Arbaugh’s cursor control.
However, New technologies often encounter initial challenges, but with dedicated effort and innovation, companies can turn these hurdles into opportunities for improvement. A prime example of this is Apple’s initial release of Apple Maps. When Apple replaced Google Maps with its own mapping technology in iOS 6, it faced widespread criticism for inaccuracies and poor quality of the maps. Apple quickly acknowledged the issues and dedicated significant resources to improving the maps, including hiring new technology experts and acquiring companies with mapping technology. Over time, Apple Maps significantly improved and is now a credible competitor to Google Maps.
Google DeepMind’s updated AlphaFold now has the capability to model a significantly broader range of biological life.
Google DeepMind has unveiled an advanced version of its biological prediction tool, AlphaFold, now capable of modeling not only protein structures but nearly all biological elements. This enhancement could significantly boost the speed of drug discovery and other scientific endeavors. Currently, the tool is being applied to a range of experiments, from developing more resilient crops to formulating new vaccines.
The initial version released in 2020 captured the attention of the scientific community with its proficiency in predicting protein structures. Since then, researchers have expressed a strong desire for the tool to extend its capabilities beyond proteins.
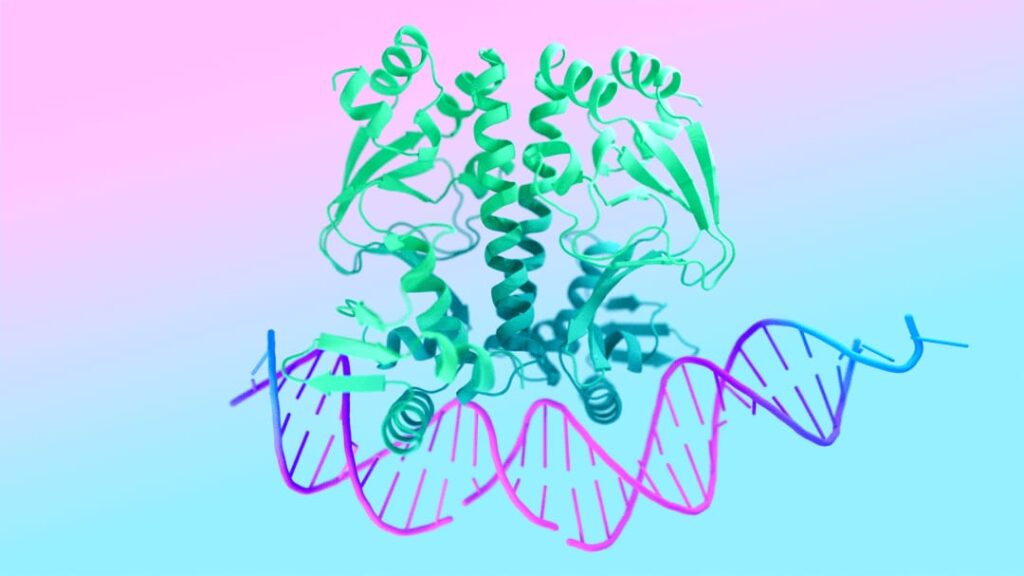
According to DeepMind, the latest iteration, AlphaFold 3, is equipped to predict the structures of DNA, RNA, and critical molecules such as ligands, which play a vital role in drug discovery. DeepMind claims that this version provides a more intricate and dynamic view of molecular interactions than any previous tool.
DeepMind CEO Demis Hassabis emphasized the dynamic nature of biology during a press call, noting that biological properties emerge from the interactions of various molecules within a cell. He described AlphaFold 3 as a significant step towards modeling these complex interactions.
While AlphaFold 2 contributed to advancements such as mapping the human heart, modeling antimicrobial resistance, and identifying the eggs of extinct birds, the full potential of AlphaFold 3 remains to be seen.
Mohammed AlQuraishi, an assistant professor of systems biology at Columbia University who is not affiliated with DeepMind, believes the updated model will greatly enhance drug discovery capabilities. He pointed out that the previous system was limited to amino acids, restricting its utility for biopharmaceutical applications. However, the new version is theoretically capable of predicting how a drug interacts with a protein.
New Standards Allow Users to Verify Sources of AI-Generated Content !
OpenAI has joined the Steering Committee of the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA), a widely recognized standard for digital content certification. This standard, developed with contributions from software companies, camera manufacturers, and online platforms, allows for the verification of content origins. OpenAI is eager to contribute to the further development of this standard, viewing it as a crucial component of its strategic approach.
Earlier in the year, OpenAI began incorporating C2PA metadata into all images created and edited by DALL·E 3, its most recent image model, utilized in ChatGPT and the OpenAI API. The company also plans to integrate C2PA metadata into Sora, its upcoming video generation model, once it is released more broadly.
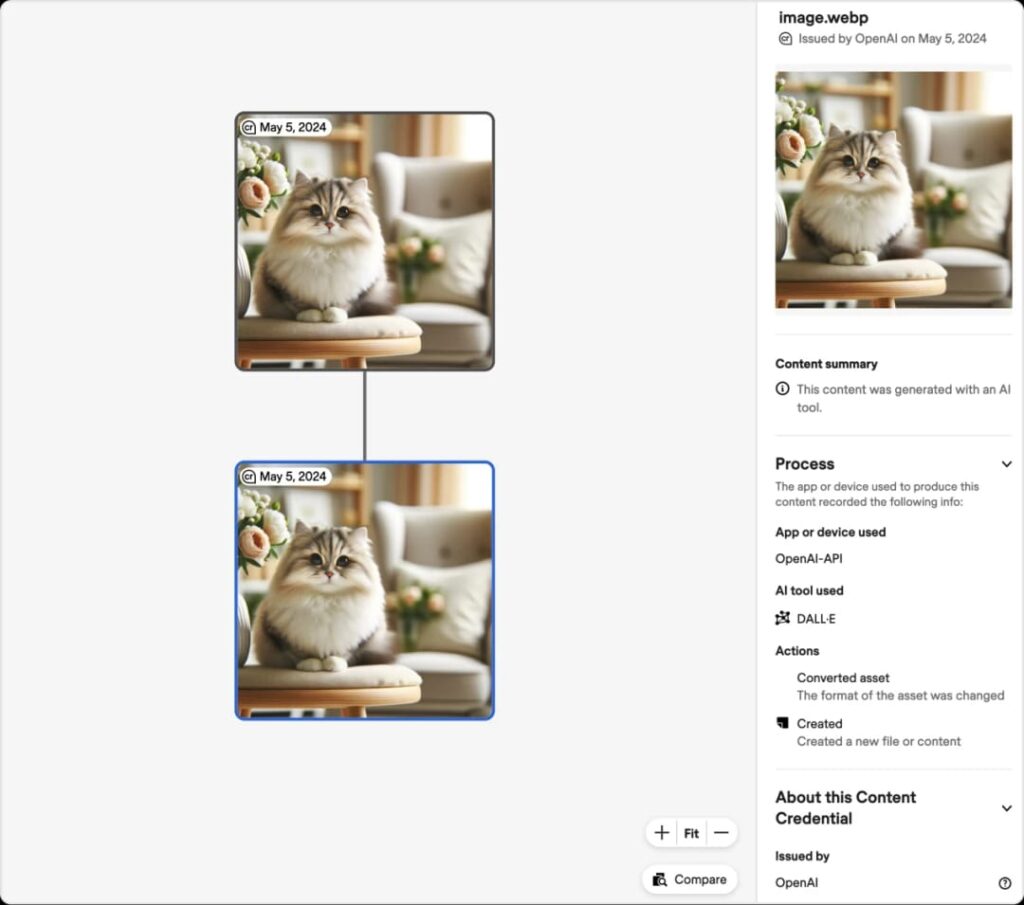
In addition to its involvement with the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA), OpenAI is advancing new methods to ensure the integrity of digital content. This includes the development of tamper-resistant watermarking, which involves embedding an invisible signal into digital content such as audio, designed to be difficult to remove. Additionally, OpenAI is creating detection classifiers, which are AI tools designed to evaluate whether content was likely generated by AI models. These innovations aim to make it harder to erase indicators of content’s origins.
The introduction of tamper-resistant watermarking and detection classifiers represents a proactive approach to address the growing concerns around the authenticity and origin of digital content, particularly as AI-generated materials become more pervasive.
These technologies not only aim to protect content creators and consumers from potential misuse but also contribute to establishing a trustworthy digital environment. By making it more challenging to remove signals indicating the origin of content, OpenAI enhances transparency and accountability, which are crucial in maintaining public trust in AI technologies.
OpenAI Set to Unveil Game-Changing Search Feature for ChatGPT, Directly Challenging Google’s Dominance
According to multiple sources, OpenAI is poised to announce a new search feature for ChatGPT this Monday, which will put it in direct competition with Google Search and Perplexity. This new functionality will allow ChatGPT to access online sources to answer user queries, providing citations for the information used. Additionally, some versions of this feature may include relevant images alongside text responses, such as diagrams or illustrated instructions.

Currently, OpenAI offers limited browsing capabilities to ChatGPT Plus subscribers, but this has been plagued with inconsistencies and bugs. The launch of this search feature is particularly significant as it comes just a day before Google I/O, marking a major escalation in the AI competition between OpenAI and Google. This enhancement could also elevate ChatGPT’s capabilities, opening the door for more advanced, agent-like features.
The timing of this announcement, just before Google I/O, could be seen as a strategic move by OpenAI to position itself as a frontrunner in the AI space. This new functionality could transform ChatGPT from a conversational AI into a more comprehensive information retrieval tool, which is crucial as users increasingly seek more sophisticated, accurate, and actionable AI interactions. The development of these features also hints at a future where AI not only assists with simple tasks but acts more autonomously, providing a gateway to more advanced applications and possibly reshaping how everyday users interact with AI technologies.
